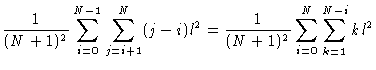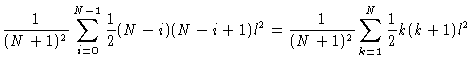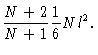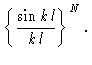



Next: Appendix C
Up: The Gaussian chain
Previous: Appendix A
In the case of the freely jointed chain both the angles 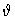 and
and 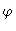 are
completely random. Then
are
completely random. Then
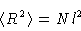 |
(3.45) |
A simple trick exists to calculate all the moments of the chain. To this
end, look at the Fourier transform
The prime at the summation sign in the last but one line indicates that only
terms with even n should occur in the sum. Eq. (3.47)
tells us that
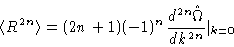 |
(3.48) |
In order to use this formula we need to know
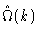 .
Inverting
Eq. (3.5) we get
.
Inverting
Eq. (3.5) we get
Although the trick is nice, the task to evaluate the derivations is rather
tedious.




Next: Appendix C
Up: The Gaussian chain
Previous: Appendix A
W.J. Briels
![]() and
and ![]() are
completely random. Then
are
completely random. Then